Comments on Lyndale Pond comments (and a very hard quiz on Minneapolis parks)
If you’re interested in the subject of a pond near Lyndale and Franklin, you might want to check out “comments” on the subject posted a few days ago. Some good information. Thanks to readers who responded and to Cheryl Luger for posing the questions in the first place.
I wanted to add that while investigating another subject I found an 1897 Minneapolis map produced by the city engineer that shows elevations. (A small section of that map is pictured below.) It’s also interesting to see where in the city you could get running water and why the city was installing water lines from a reservoir in Columbia Heights. Note the highest elevations in the city. To keep things in perspective the population of Minneapolis in 1900 was already more than 200,000. The 1890s was the first decade in four in which the population of Minneapolis didn’t nearly triple. Likely due to the depression set off in 1893.

Detail of 1897 Minneapolis map that shows parks, elevations, water lines and street car lines. (James K. Hosmer Special Collections Library, Hennepin County Library)
The complete map, as well as dozens more from around the state, are available at the Minnesota Digital Library, an excellent resource for researchers or the curious.
Unfortunately, this map has less topographical detail than the map suggested by Bill Payne in his comment on the previous article. It shows no remnant of the pond on earlier maps at Lyndale and 22nd, nor the depression that is noted there on the 1901 map Bill found. The 1897 city map shows elevation increments of 25 feet; the 1901 map shows increments of 20 feet, which may account for the difference.
Here’s the quiz
Many, many properties were added to the Minneapolis park system after this map was made in 1897. For instance, notice that there is no West River Parkway, nor a St. Anthony Parkway, nor a Victory Memorial Drive, and on and on. Most of the Grand Rounds hadn’t been built. (This map doesn’t even show Stinson Parkway, which did exist in 1897!) But there are three significant park properties on this map that are no longer park properties. Can you name them?
Click on “complete map” above, then zoom into various sections of the city to find the long-gone pieces of the park system. All were no longer park property by 1905. (Note: The island at the south end of Lake of the Isles is a good catch, but doesn’ t count because it’s still part of the lake and park. The same goes for the northern end of Powderhorn Lake, which once extended north of 32nd; it’s still part of the park. Same for Sandy Lake in Columbia Park; the lake is gone, but it’s still a park.)
Winner gets a free subscription to minneapolisparkhistory.com!
David C. Smith
NOTE (June 1, 2012): The contest is now over and Adrienne was the winner. She named Meeker Island in the Mississippi River as one park property on the map that is no longer. The other two were Hennepin Avenue South and Lyndale Avenue North. Both were parkways in 1897, but were given up by the park board in 1905. The city subsequently took responsibility for them as ordinary city streets.
CMPC: Park Property Monuments?
This week I was included in an e-mail discussion between MaryLynn Pulscher and Annie Olson at the park board and Daniel Fearn. Daniel had found two interesting metal markers in the ground near Minnehaha Creek.
Daniel wondered if CMPC was an acronym for City of Minneapolis Park Commission. My reaction, as well as MaryLynn’s, was that wasn’t likely because the park board until 1969 always marked everything BPC for “Board of Park Commissioners.” The Minneapolis was generally understood.
A web search, however, turned up a document from a Hennepin County Survey that indicates the CMPC stamp may have been used on park board survey monuments. On that document a monument with a similar marker found at 50th and Cedar during the Minneapolis City Survey in 1937 was called a “park board monument”
Do you know the real story of the CMPC markers? Have you seen other markers like this anywhere else in the city? Were they on park boundaries? Or do I have to call the county surveyor’s office to resolve this?
Send photos if you have ’em.
David C. Smith
Raise Your Hand If You’ve Visited Cavell Park
Cavell Park is one of the marvelous neighborhood parks that make Minneapolis so livable, but I would bet that few Minneapolitans know where it is or have seen it. I thought I should promote it a bit before I leave the topic of Minneapolis parks and WWI completely. The only connection in this case is the name of the park, because it didn’t become a park until 1968.
Edith Cavell was a British nurse running a hospital in Belgium at the outbreak of World War I. When the German army invaded Belgium, Ms. Cavell helped British, French and Belgian soldiers escape capture and reach safety in the Netherlands. As a nurse, she treated Allied and German soldiers, but her aid to escaping Allied soldiers led to her arrest and a charge of treason by the German army. She was held in prison for ten weeks as her case aroused outrage and indignation around the world. It did little good: she was executed by a German firing squad. Cavell— her name rhymed with travel—became a central focus of British propaganda efforts and, together with the German sinking of the passenger ship Lusitania, was used to depict the depravity of Germans, the barbarous “Huns” of an earlier article.
With the start of the 1918 school year, at the height of the Great War, the Minneapolis school board was faced with overcrowding at Thomas Lowry School in northeast Minneapolis. The solution was to build two temporary portable school houses in the district. In December 1918, less than a month after fighting in Europe ended, the school board suggested that what had been referred to as the Thomas Lowry Annex, be named for Cavell.
Edith Cavell School was a portable school building originally at Tyler and 35th Avenue NE. The portable school was closed in 1933 and a new, modest school was built three blocks east at 34th and Fillmore. That school, pictured above, closed in 1949. (See more photos on the history pages of the Minneapolis public schools website here.)
The park board had considered acquiring the site for a playground park in 1949, but in light of a 1948 cooperative agreement between the park board and school board to develop property together, the two boards opted to build a new school and park four blocks further east instead. That development became Waite Park and School.
The school board continued to own the Edith Cavell School site until 1968, when the park board acquired it for a new neighborhood park. It was the first of four former school sites acquired by the park board from 1968 to 1976. The park board also acquired the old school sites of Margaret Fuller School (now Fuller Park), Lyndale School (Painter Park), and Corcoran School (Corcoran Park), all during the controversial tenure of Robert Ruhe as superintendent of Minneapolis parks. A recreation shelter was built in the park in 1977. (I hope to write a good deal more about Ruhe. His style was abrasive, but his accomplishments were undeniable.)
For those of you who live in south or north Minneapolis and rarely venture across the river, I’d suggest a drive, hike or bike ride into northeast to visit Cavell Park. Audubon and Windom parks are worth visits too. They are all quite different from the mostly flat parks of south and north Minneapolis. If you are considering a bike ride, I’d recommend it only if you are a fairly strong rider because the hills of northeast could be difficult for some. The highest elevation in the city of Minneapolis is near Waite Park, so you’ll enjoy a good climb from the river.
Do you have a story about Cavell Park — or any of the great northeast neighborhood parks? We’d love to hear it as a coment on tis page. If you have photos, let me know; e’d love to see them.
David C. Smith
A Challenge for Wedge and Whittier Historians
A regular reader has asked a couple questions that I can’t answer, but perhaps someone else can. Why does Lyndale Avenue South from 19th to 24th street or so seem to run in a trench with the east-west cross streets rising steeply on both sides of Lyndale. Is there a geological explanation for it?
Also, was there ever a swampy area at Franklin and Lyndale, or nearby in Whittier, that was drained for park purposes? The park board was never involved in such an action, but perhaps an effort to create a playground or other playing field could have taken that direction before the park board took responsibility for playgrounds.
In the 1880s there was a baseball stadium that seated about 1300 near 17th and Portland, according to Minnesota baseball historian Stew Thornley, but that’s quite a distance east. Horace Cleveland was likely referring to that field when he wrote to William Folwell in 1884, “There’s no controlling the objects of men’s worship or the means by which they attain them. A beautiful oak grove was sacrificed just before I left Minneapolis to make room for a baseball club.” Cleveland’s words imply a clear dividing line between parks and playing fields. At that time, the two did not mix. (Folwell Papers, Minnesota Historical Society.)
The area a couple blocks northeast of Franklin and Lyndale—south of what became Loring Park—was the site selected by Charles Loring, William King, Dorilus Morrison and others for a private cemetery in the 1860s. Land speculators got wind of the plan, however, and drove the price of the land higher than the cemetery group would pay. Instead they looked for land further south and established Lakewood Cemetery in 1871 at its present site. Charles Loring wrote in a letter to George Brackett, both were among the founders of Lakewood, that the idea for a beautiful cemetery came to Loring as he buried his infant daughter in Layman’s Cemetery in 1863. (George Augustus Brackett Papers, Minnesota Historical Society.)
(Ask me a question about Minneapolis parks and I’ll probably work Loring and Cleveland into the answer!)
Any ideas on the topography of Lyndale Avenue South? Or a drained swamp near Lyndale and Franklin or elsewhere in Whittier?
David C. Smith
Who, Exactly, Were the “Huns”?
Discussions of Minneapolis during World War I in a recent post have pointed to another factor that may have reinforced the willingness of the park board to sell the first Longfellow Field to Minneapolis Steel and Machinery as the company expanded to fulfill military contracts: Theodore Wirth, the superintendent of Minneapolis parks was a German speaker and, based on newspaper accounts from early in his tenure as parks superintendent in Minneapolis, he spoke English with a German accent.
Not only did the president of the park board, Francis Gross, have close ties to German immigrants and descendants as president of the German-American Bank, and, presumably spoke German, based on accounts of his speeches, but the park board’s top administrator, Wirth, who was from Winterthur, Switzerland, only several miles from the German border, also spoke German. Seems suspicious, nein?
Even though Wirth had immigrated to the U.S. thirty years earlier, was not from Germany, and Switzerland was neutral during the war, I don’t know if those distinctions were known or made by most people. Could someone like Wirth have felt pressure to profess or demonstrate his “loyalty” to the U.S.—perhaps by agreeing to the sale of park land to a growing munitions maker?
Remember those were days of loyalty oaths, “Americanization” meetings, and arrests of “enemy aliens.” I recently read that the director of the Boston Symphony Orchestra, German-born Karl Muck, was arrested as an enemy alien in Cambridge, Massachusetts in March, 1918. He was accused of nefariously featuring too many German composers in his programs—damn that Beethoven!—and was suspected of using his score markings as a secret code. His claim that he was a naturalized citizen of Switzerland proved true, but didn’t keep him from being locked up in a prison camp in rural Georgia for 17 months. He had been offered a conducting job once by Kaiser Wilhelm. He was kept in prison for ten months after the end of the war that made the world safe for democracy, perhaps to ensure that he wouldn’t detonate a lethal Eroica in a crowded concert hall.
Wirth’s native tongue and the proximity to Germany of his hometown may have had no bearing on his standing in Minneapolis or on park board actions during WWI, but in a world where musicians could be locked up for their taste in fugues, it is not out of the question that it crossed someone’s mind. Especially when you read of speeches like those of former President Theodore Roosevelt on a stop in Minneapolis in October 1918. Minneapolis Tribune reporter George E Akerson wrote on October 8:
Theodore Roosevelt, American’s foremost private citizen, yesterday preached his gospel of thorough-going Americanism, to more than 15,000 persons in Minneapolis. At five different meetings, the former president, exhibiting all of his old time aggressiveness, delivered his message, never missing an opportunity to pillory the “Huns within our gates” along with the “Huns without.”

Theodore Roosevelt addressing more than 5,000 workers at Minneapolis Steel and Machinery, October 7, 1918. As WWI neared its end, Roosevelt urged vigilance against the “Huns within.” His black armband signified that he had lost a son in the war. (Minnesota Historical Society.)
Roosevelt was not referring specifically to Germans as much as to those he perceived as enemies of the U.S government, but that would have been a fine distinction to those reading the lead quoted above. The taint of all Germans, past and present, could easily be inferred. One of Roosevelt’s five speeches in his one-day stop in Minneapolis was at the munitions factory of Minneapolis Steel and Machinery, pictured above.
The derogatory “Hun” to describe Germans was derived from the Huns of Attila fame and equated with “barbarian.” Germans and Huns had little in common historically, but the term was a staple of Allied propaganda during the war. Some older warriors, such as Winston Churchill and Franklin Roosevelt, stuck with the term in WWII, but “Krauts” became the more popular alternative.
David C. Smith
Longfellow Field: The Park that Bombs Bought
If any park in Minneapolis should be a “memorial” park, perhaps it should be Longfellow Field, because it was bought and built with war profits. It would be hard to explain it any other way. The neighborhood around present-day Longfellow Field is one of the few in the city that didn’t pay assessments to acquire and develop a neighborhood park. That’s because the park board paid for it with profits from WWI.
The story begins with the first Longfellow Field at East 28th St. between Minnehaha Avenue and 26th Avenue South. (There’s a Cub Store there now.) It was once one of the most popular playing fields in the city—and it is the largest playground the park board has ever sold.

The park board purchased the field in the upper right of this photo in 1911 and named it Longfellow Field. This photo, looking northwest, was taken from the top of Longfellow School at Lake St. and Minnehaha Ave. shortly before the land was purchased for a park. Minnehaha runs through the center of the photo and ends at E. 28th St. where the vast yards of the Chicago, Milwaukee and St. Paul Railway begin. Minneapolis Steel and Machinery is on the left or west side of Minnehaha. (Charles Hibbard, Minnesota Historical Society)
The origins of that field as a Minneapolis park go back to 1910 when the park board’s first recreation director, Clifford Booth, recommended in his annual report that the city needed a playground somewhere between Riverside Park and Powderhorn Park.

Clifford Booth, shown here in 1910, was the first recreation director for Minneapolis parks and an unsung hero in park history.
It was the only addition he recommended to the playground sites he already supervised around the city.
The following year, the park board found the perfect place within the area Booth suggested: an empty field just off Lake Street, about equidistant from Powderhorn and Riverside, a stones throw from Longfellow School, easily accessible by street car, and it was already used as a playing field. The park board purchased the 4-acre field in 1911 for just over $7,000 and spent another $8,000 to install football and baseball fields, tennis, volleyball and basketball courts, and playground equipment.
An architect was hired to create plans for a small shelter at the south end of the park, but when bids for the shelter came in at more than $10,000, double what park superintendent Theodore Wirth had estimated, the park board decided it couldn’t afford the shelter.
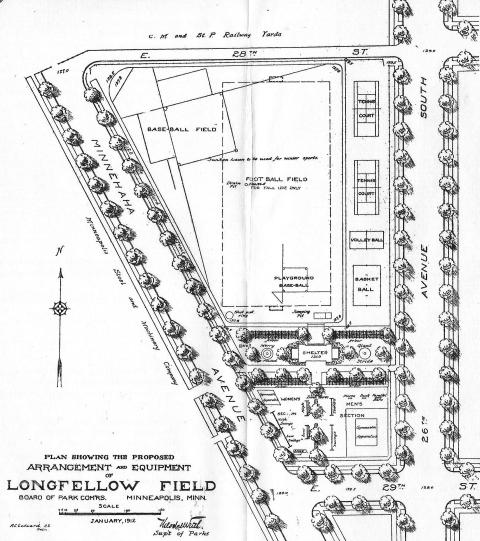
This plan for the development of Longfellow Field was published in the 1911 Annual Report of the park board. (Minneapolis Park and Recreation Board.)
Despite the absence of a shelter, Wirth wrote in 1912 that Longfellow was one of the most active playfields in the city. Longfellow Field and North Commons were the venues for city football and baseball games for two years while the fields at The Parade were re-graded and seeded. The popularity of the field was attested to by the police report in the 1913 annual report of the park board, which claimed that additional police presence was necessary to control the crowds at football games at Longfellow Field and North Commons.
This Is Where the Intrigue Begins
I was surprised when I learned that the park board sold the park in 1917. The park board had never sold a park before. Why then—after 34 years of managing parks? And why this park? The park board’s explanation in the 1917 annual report was pretty weak, stating only that the field “became unavailable for a playground on account of the growth of manufacturing business in the vicinity.” The property was already on the edge of an industrial zone—see photo above—when it was purchased, so this was no revelation.

Longfellow School, on Lake Street and Minnehaha Avenue, was built in 1886 and used until 1918. (Minnesota Historical Society)
The park board resolution on October 17, 1917 to sell the land provided a bit more explanation, but it still seemed less than forthcoming. It wasn’t just the growth of manufacturing business, the resolution claimed, it was also the school board’s decision to close Longfellow School and build a new school farther south. Moreover, the park board claimed that to make the playground useful it would be necessary to invest in improvements and a shelter. Given the other shortcomings of the site, the park board didn’t think it prudent to make those investments at that site.
So the park board declared that the site was no longer useful for a park, a legal requirement to get district court permission to sell the land, and it was sold for $35,000 to the Minneapolis Steel and Machinery Company.
At the time the park board decided to sell the field it also expressed its intention to find a “more suitable area” for a park and playground nearby in south Minneapolis. Less than two weeks after the sale was announced, the board designated land for a second Longfellow Field, the present park by that name, about a mile southeast in a much less populated neighborhood. The park board paid the $16,000 for the new land—not just four acres, but eight—and for initial improvements to the park from the proceeds of the earlier sale. It was a boon for property owners in the vicinity of the new Longfellow Field: a new park without property assessments to pay for it. The owners of three houses that had just been built across the street from the park must have been thrilled.
When I learned all of this a few years ago, I assumed that in the end the land deal was about the money—the opportunity to sell for $35,000 land the board had bought only six years earlier for $7,000. Even if you subtract the $8,000 spent on improvements, that was a nice return. And to keep that sum in context, remember that the park board shelved plans for a park shelter when bids exceeded estimates by $5,000. Thirty-five grand was a lot of money for a cash-strapped park board.
But the deal still puzzled me, especially because of the unusual way the transaction was introduced in park board records.
Park board proceedings, October 9, 1917, Petitions and Communications:
“From the Minneapolis Steel and Machinery Company —
Asking the Board to name a price at which it would sell the property included in the tract of park lands known as Longfellow Field.”
Talk about asking to be gouged! Who starts negotiations that way? Name a price? That seemed fishy. So did the speed of the deal. Two committees were asked to report back on the issue the following week, the first indication that someone was in a big hurry to get a deal done. The joint committees not only reported back a week later, they had come up with a price, $35,000, and had essentially concluded the deal. There hadn’t been time for much dickering over the number; the park board had a very motivated buyer. Moreover the board selected land to replace Longfellow Field only two weeks later. As decisive as early park leaders often were, this was unprecedented speed. Too much money. Too fast. Too little explanation.
Perhaps too little deduction on my part as well, but that’s where the matter stood for me the last few years until I decided recently to look into it a bit more as I was compiling a list of “lost parks” in Minneapolis. What I learned is that the decision to sell Longfellow Field had less to do with demographic shifts or manufacturing concentration in south Minneapolis than what was happening in the fields of France and the waters of the North Atlantic.
The United States Joins a World at War
For more than two years, the United States had stayed out of the Great War that embroiled much of the rest of the world. But in early 1917 Germany took the risk that a return to unrestricted submarine warfare and a blockade of Great Britain, including attacks on American ships, could bring about an end to the war before the United States could mobilize its army and economy to have a significant impact on the ground war in Europe. Germany knew that its actions would bring the U.S. into the war—and they did. The U.S. Congress declared war on Germany on April 6, 1917—and began to mobilize in earnest. Part of that mobilization was the enactment of the selective service, or draft, law in May 1917 to build an army. Another part was the procurement of weapons and equipment needed to fight a war.
Of course the manufacturing capacity for war couldn’t be built from scratch. Existing expertise, process and capacity had to be converted to war products. That meant beating plowshares into swords.
That’s where Minneapolis Steel and Machinery came in. In the fifteen years since its founding, Minneapolis Steel had become one of the leading suppliers of structural steel for bridges and buildings in the northwest. That was the “steel” part of the name. The “machinery” was represented most famously by Twin City tractors, but also by engines and parts it manufactured for other companies.

Doesn’t the logo for a line of products from the Minneapolis Steel and Machinery Company remind you of the logo of our favorite boys of summer? (Thanks to Tony Thompson at twincitytractors.tripod.com)
All I knew about Minneapolis Steel and Machinery was that in the 1920s it was one of the companies that merged to become Minneapolis-Moline and that it was notoriously anti-union. I didn’t know that it was an important military supplier, too.
The first evidence I found of the company’s production for war was a November 10, 1915 article in the Minneapolis Tribune that claimed the company would begin shipping machined six-inch artillery shell casings to Great Britain by January 1, 1916. The paper reported that the initial contract, expected to be only a trial order, was for almost $1.5 million.
Less than two weeks later, another Tribune report made it clear that the company’s involvement in the war was much broader. The paper reported on November 23 an order from Great Britain for 100 tractors from Bull Tractor, another Minneapolis company, for which Minneapolis Steel did the manufacturing and assembly. The tractors, still a relatively new invention, would be shipped from Great Britain to France and Russia to supplant farm horses drafted for war service or already killed in the war. Minneapolis Steel was also shipping 50 steam shovels to be used to dig trenches on the Russian front. Both orders were placed by the London distributor for both Minneapolis Steel and Machinery and Bull Tractor.
Shell orders must have continued for Minneapolis Steel and Machinery after the initial order in 1915, too, because on August 16, 1917 the Tribune reported a new order for the company. Under the headline, “Steel and Machinery Plant to Be Enlarged to Meet Uncle Sam’s Demand for Shells,” the paper reported,
“War orders just taken will necessitate a considerable enlargement of the buildings of the Minneapolis Steel & Machinery company. The company, after completing its shell contract with the British government last spring, decided not to accept any more shell orders, but the United States insisted and a large contract is the result.”

Artillery played an unprecedented role in a war in which both sides were dug into trenches. Blanket bombardments preceded most offensive actions. The result was a French countryside that resembled nothing earthly.
The report, which quoted Minneapolis Steel vice president George Gillette, continued that the company was also manufacturing steam hoists for ships and expected more contracts as the building program progressed. More contracts, unsolicited according to Gillette, did indeed materialize in the next month for carriages for 105 millimeter guns and steering engines for battleships. Those contracts reportedly required a doubling of the company’s manufacturing capacity. At that time government contracts accounted for 75 percent of the company’s output. By early 1918, the Tribune reported that Minneapolis Steel and Machinery had already been awarded $23 million in government contracts.
In the midst of this rash of new military contracts, Minneapolis Steel asked the park board to name its price for Longfellow Field. Even before the district court finished its hearings on the park board’s proposed sale, the company had obtained building permits for three new warehouses, two of them in the 2800 block of Minnehaha Ave., a short foul pop-up from home plate at the former Longfellow Field.
A Civic Duty
The spirit of the times suggests that while money may have been a factor in the park board’s prompt action, it likely was not the primary motivation for selling Longfellow Field. The park board probably viewed the sale as its civic and patriotic duty to assist the war effort—especially given the other valid reasons for moving the playground.
An example of the patriotic fervor generated by the war—to which park commissioners could not have been immune—was a dinner held at the Minneapolis Club, June 12, 1917, to raise funds for the American Red Cross, which was preparing field hospitals to treat wounded soldiers. (Did the army not have a medical or hospital corps?) The next morning the Tribune reported that in one hour the 200 business and civic leaders at the dinner pledged more than $360,000 to the Red Cross. That amount eclipsed the city’s previous one-evening fund-raising record of $336,000 for the building fund for the Minneapolis Institute of Arts a few years earlier.
The report is noteworthy especially for the accounts of the number of men present, among the wealthiest and most influential citizens of Minneapolis, who had sons and nephews on their way to France—so different from the wars of the last four decades.
“Almost every man who rose to name his contribution had a son already in France or on his way. So often did the donor, in making his contribution, add that his boy was wearing the khaki of the army or navy blue that Mr. Partridge (the emcee of the evening) called the roll to ascertain just how many present had sons or nephews in the service. Including two who announced that they themselves were entering the service, the total was 56—mostly sons.”
One of the two men present who was entering military service himself was introduced as Dr. Todd, son-in-law of J. L. Record, who was president of Minneapolis Steel and Machinery. Record pledged $10,000 to the Red Cross on behalf of his company that night.

Ernest G. Wold was one of two WWI pilots from Minneapolis who died in the air over France. The other was Cyrus Chamberlain. (Minnesota Historical Society)
Among others who pledged money were two bankers who had sons in the military aviation services, F. A. Chamberlain, chairman of First and Security National Bank, and Theodore Wold, governor of the Minneapolis Federal Reserve Bank. Both men—and Chamberlain’s wife—were leaders in raising funds for the Red Cross and in selling Liberty Bonds. Their sons never came home. Ernest Wold and Cyrus Chamberlain died in the air over France in 1918. They were jointly honored by having Minneapolis’s airport named Wold-Chamberlain Field, a name that still stands. This was several years before the Minneapolis park board assumed control of building and operating the airport.
The Park Board During the War
Also making pledges at the Minneapolis Club dinner were park commissioners William H. Bovey and David P. Jones. Two other park commissioners who took active roles in the war effort were Leo Harris who resigned from his seat on the park board to enlist and Phelps Wyman who took a leave of absence from the park board to serve as a landscape architect for a group designing new towns for the workers needed at military factories and shipyards.
But it was the president of the park board in 1917 who had the most to lose—or prove—during those days of heated anti-German rhetoric. Francis Gross was the president of the German-American Bank in north Minneapolis. Gross had worked his way up from messenger to the presidency of the bank, which was said to be the largest “non-centrally located” bank in Minneapolis. The bank, founded in 1886, had been located on the corner of Plymouth Avenue and Washington Avenue North since 1905. Gross eventually served 33 years as a park commissioner between 1910 and 1949, earned the nickname “Mr. Park Board,” and had a Minneapolis golf course named for him. He must have been indefatigable, because his name pops up in association with many civic and financial endeavors.
Of all the park commissioners in Minneapolis history, Frank Gross is one of the most intriguing to me. If I could find some cache of lost journals of any of the city’s park commissioners since Charles Loring and William Folwell, I would most want to find those of Frank Gross. He’d be a great interview subject.
In the second year of the war, before the U. S. entry into the conflict, Gross was quoted in the Tribune expressing his view that Germany’s desire for peace was “sincere.” He urged the U. S. and other neutrals to push for peace. “I have no sympathy with the assertion that one side must be victor,” he said. “There can be a fair settlement now on nationality lines.”
Gross’s role in the war effort changed considerably after the U.S. entered the war. The tension of war in the U.S. was underscored when in March 1918, the German-American Bank officially changed its name to North American Bank. Gross asserted that the old name no longer represented the bank’s business or clients, adding “it is not good or desirable that the name of a foreign nationality be attached to an American institution.” In announcing the name change, Gross emphasized that his bank had been the first Minnesota bank to join the federal reserve system in 1915 “to do its part to establish a national banking system in our country so strong and efficient that it could meet any demand our country might make upon it.” (Tribune, March 8, 1918.) Gross’s implicit message: those demands could even include making war on the fatherland of the bank’s founders.
Only three weeks after Gross’s bank changed its name, he went on a speaking tour of towns outside Minneapolis that had large populations of German immigrants or descendants. The Tribune described his visit to Waconia on March 28, 1918. “In line with the belief of the state war savings and Liberty Loan committees that there is a distinct desire in German communities to have the war explained by persons of German birth or descent, Frank A. Gross, president of the North American bank, has spoken to several meetings composed entirely of Germans in the last few days,” the Tribune’s report began. Gross told of how he had circulated among the estimated crowd of 300 people of German descent, mostly farmers, before he spoke and found a “feeling that anyone of German birth or German descent is not wanted as a citizen of this country.”
He ascribed the feeling to the manner in which “overzealous orators” had attacked the German people, “not distinguishing between German imperialism, against which we are making war, and the German people.” Gross said that he then told the people of Waconia they “certainly were wanted as American citizens, but that the citizenship carried with it the responsibility of 100 per cent loyalty to this nation.” Gross said he also dispelled the notion that this was a “rich man’s war,” asking if they thought the “rich would send their boys to war just so their fathers could make a little more money.”
Family experience: My father, who grew up in a small town in rural Minnesota, recounts that his older brother and sister, born before WWI, spoke primarily German before they went to school, but my father and another sister, born after WWI, were never taught German.
Gross later was a prominent speaker at meetings promoting the purchase of Liberty bonds, especially in predominantly German communities such as New Ulm, Hutchinson and Glencoe, and he spoke at “Americanization” meetings—scheduled in Minneapolis neighborhoods with large “foreign elements” according to the Tribune—about “Patriotism.” He shared the podium at one such meeting in north Minneapolis with Rabbi S. M. Deinard whose subject was “The Obligation of the New Generation to the Old” and Mr. E. Avin of the Talmud Torah who gave a patriotic address in Yiddish. Gross also became an instructor, along with future Minneapolis mayor Wallace Nye, at a school for Minneapolis draftees before they were sent off to military camps.
The park board’s annual reports written while Gross was president of the board in 1917 and 1918 reveal very little of the impact of war on parks other than brief references to the heavy burden of taxes and contributions to welfare organizations and the lack of funds for park maintenance. From Gross’s other activities, however, as well as those of other park commissioners, it is apparent that the board would have had a strong sense of patriotic obligation to do what it could to assist the war effort. And that certainly extended to providing expansion space for one of Minneapolis’s largest military suppliers. So the original Longfellow Field became a casualty of war—and the neighborhood surrounding the new Longfellow Field acquired a park without having to pay property assessments.
The Last Link
One connection remains between the descendants of Minneapolis Steel and Machinery and Minneapolis parks. Minneapolis Steel and Machinery built Bull tractors, but the engines were supplied by another local company, the Toro Motor Company. Bull, Toro, get it? One contemporary newspaper account (November 17, 1918), describes Toro as a subsidiary of Minneapolis Steel and Machinery, but the website of The Toro Company today does not claim that connection. (The Toro website does claim the company produced steam steering engines for ships during WWI, however, a product that newspaper reports in 1917 attributed to Minneapolis Steel and Machinery.) Regardless of legal relationship, the two companies were closely connected and Toro is the sole survivor of the Bull, Minneapolis Steel, and Toro tractor trio.
Toro later focused its efforts on lawn-care products, famously lawn mowers, and still specializes in turf management products mostly for parks, athletic fields and golf courses. Each year in recent times, Toro and its employees, along with the Minnesota Twins Community Fund, have donated the materials, expertise and labor to rehabilitate or upgrade a baseball field in a Minneapolis park. These little gems of ball parks now exist in several Minneapolis parks, from Stewart Park to Creekview Park. Thank you, Toro. I don’t know specific park board needs now, but wouldn’t it be appropriate if Toro helped put in a fabulous field at Longfellow Park in honor of the connection long ago?
I’ll leave the final word on WWI in Minneapolis to a preacher.
“I rejoice that I am no longer needed as a partner in the grim business of killing.”
— Rev. Elmer H. Johnson, pastor of Morningside Congregational church who had worked for 11 months at the artillery shell factory of Minneapolis Steel to augment his church salary. (Minneapolis Morning Tribune, December 22, 1918)
David C. Smith
NOTE: Bob Wolff of The Toro Company provides additional details on that company in a “Comment” on the David C. Smith page. (May 31, 2012). In a separate note, Bob said he’d also look into finding photos of the first Toro turf management products used in Minneapolis parks. Stay tuned.
© David C. Smith
Canoe Jam on the Chain of Lakes
The newspaper headline hinted of a sordid affair: “Long Line Waits Grimly in Courthouse Corridor.” Many were so young they should have been in school. Others had skipped work. They stood anxiously in the dim hallway, waiting. News accounts put their numbers at 500 when the clock struck 8:30 that April morning. Many had already been there for hours by then. They prayed they would be among the lucky ones to get permits to store their canoes at the most popular park board docks and on the lower levels of the lakeside canoe racks, so they wouldn’t have to hoist their dripping canoes overhead.
The year was 1912 and nearly 2,000 spaces were available on park board canoe racks and dock slips at Lake of the Isles, Lake Calhoun and Lake Harriet. Nearly all of them were needed, which represented a huge increase over the 200 permits issued only two years earlier. The city was canoe crazed.
By contrast, in 2011 the park board rented 485 spaces in canoe racks at all Minneapolis lakes, in addition to 368 sail boat buoys at Calhoun, Harriet and Nokomis.

Canoeing was extremely popular on city lakes, especially after Lake of the Isles and Lake Calhoun were linked by a canal in 1911, followed by a link to Cedar Lake in 1913. (Minnesota Historical Society)
The demand for canoe racks was so great that park superintendent Theodore Wirth proposed a dramatic change at Lake Harriet at the end of 1912 to accommodate canoeists.
Wirth’s plan (above), presented in the 1912 annual report, would have created a five-acre peninsula in Lake Harriet near Beard Plaisance to accommodate a boat house that would hold 864 canoes. The boat house would have been filled with racks for private canoes, as well as lockers for canoeists to store paddles and gear. The boat house, in Wirth’s words, “would protect the boat owners’ property, and would relieve the shores of the unsightly, vari-colored canoes.”
The board never seriously considered building the boat house and that summer the number of watercraft on Lake Harriet reached 800 canoes and 192 rowboats. Most of the rowboats and about 100 of the canoes were owned and rented out by the park board. Even more crowded conditions prevailed at smaller Lake of the Isles where the park board did not rent watercraft, but issued permits for 475 private canoes and 121 private rowboats.

Rental canoes were piled up on the docks near the pavilion at Lake Harriet ca. 1912. (Minnesota Historical Society)
The park board’s challenge with so many watercraft wasn’t just how to store them, but how to keep order on the lake. An effort to maintain decorum on city lakes began in April 1913 when another year of permits was issued. The park board announced before permits went on sale that because of “considerable agitation about objectionable names” on boats and canoes the year before, permits would not be issued to canoes that bore offensive names.
The previous summer newspapers reported that commissioners had condemned naughty names such as, “Thehelusa,” “Damfino,” “Ilgetu,” “Skwizmtyt,” “Ildaryoo,” “O-U-Q-T,” “What the?,” “Joy Tub,” “Cupid’s Nest,” and “I’d Like to Try It.” The commissioners decided then that such salacious names would not be permitted the next year, even though Theodore Wirth urged the board to take the offending canoes off the water immediately.
When the naming rules were announced the next spring, park board secretary J. A. Ridgway was given absolute power to decide whether a name was acceptable. To begin with he allowed only monograms or proper names, but used his discretion to ban names such as “Yum-Yum” even though that was the name of a character in Gilbert and Sullivan’s “The Mikado.” Even proper names could be improper.
Despite the strict naming rules, all but 75 of the park board’s 1400 canoe rack spaces were sold by late April, and practically all remaining spaces were “uppers” scattered around the three lakes.
The crackdown on canoe-naming wasn’t the end of the park board protecting the morals of the city’s youth on the water however. Take a close look at the 1914 photo below by Charles Hibbard from the Minnesota Historical Society’s collection.
The photo shows canoeists listening to a summer concert at the Lake Harriet Pavilion. Notice the width of the typical canoe and how two people could sit cozily side-by-side in the middle of the canoe. Now imagine how easy it would be to drift into the dark, get tangled up with the person next to you and make the canoe a bit tippy. Clearly a safety issue.
The Morning Tribune announced June 28, 1913 that the park board would have no more of such behavior. “The park board decided yesterday afternoon, ” the paper reported, “that misconduct in canoes has become so grave and flagrant that it threatens to throw a shadow upon the lakes as recreation resorts and to bring shame upon the city.”
The solution? A new park ordinance required people of opposite sex over the age of 10 occupying the same section of a canoe to sit facing each other. No more of this side-by-side stuff, sometimes recumbent. According to the paper, park commissioners said the situation had become one of “serious peril to the morals of young people.” Park police were given motorized canoes and flashlights to seek and apprehend offenders.
The need for flashlights became evident after seeing the park police report in the park board’s 1913 annual report. Sergeant-in-Command C. S. Barnard, referring to the ordinance that parks close at midnight, noted a policing success for the year. To get canoeists off the lake by midnight, the police installed a red light on the Lake Harriet boat house that was turned on to alert lake lovers that it was near 11:30 pm, the time canoes had to leave the lake. Barnard reported that the red light “has been a great help in getting canoeists off the lake by 11:30 p.m., but owing to the large number who stay out past that time (emphasis added), I would suggest that the hour be changed to 11 o’clock in order to enable the parks to be cleared by 12 o’clock.”
Indignant protest against the side-by-side seating ban arose immediately. Arthur T. Conley, attorney for the Lake Harriet Canoe Club, suggested that the park board show a little initiative and arrest those whose conduct was immoral rather than cast a slur on “every woman or girl who enters a canoe.” If Conley believed the ordinance was a slur on men and boys as well he didn’t say so, but he did add, “We dislike to hear that we are engaged in a sport which is compared with an immoral occupation and that we are on the lake for immoral purposes.”
In the face of protests, the new ordinance was not vigorously enforced and was repealed before the start of the 1914 canoe season. The Tribune noted in announcing the repeal that “the public did not take kindly to the ordinance last year and boat receipts at Lake Harriet fell off considerably on account of it.”
Despite the repeal of the unpopular ordinance, boating fell off even more in 1914. In the annual report at the close of the year Wirth attributed the decline partly to a terrible storm that passed over Lake Harriet on June 23 resulting in the drowning of three canoeists. Newspapers reported dramatic rescues of several others. By 1915 the number of canoe permits had dropped under 1400 even though canoe racks had been added to Cedar Lake, Glenwood (Wirth) Lake and Camden Pond.
The popularity of canoeing continued to decline. Wirth noted in 1917 that there had been a very perceptible decrease again in the number of private boats and canoes on the lakes. While he attributed that decline partly to unfavorable weather, he also noted the “large number of young men drawn from civil life and occupations to military service” as the United States entered WWI.
There were only six sail boats on city lakes in 1917, and all six were kept on Lake Calhoun. The first year that the park board derived more revenue from renting buoys for sail boats than racks for canoes was not until 1940. From then until now sailing has generated more revenue for the park board than canoeing.
The number of canoe permits leveled off for a while in the 1920s at about 1000 per year, but the canoe craze on the lakes had passed, much as the bicycle craze of the 1890s. During the bicycle craze the park board had built a corral where people could check their bikes while at Lake Harriet. That corral held 800 bicycles. At the peak of the much shorter-lived canoe craze in the 1910s, the park board provided rack space at Lake Harriet for 800 canoes. Popular number. Fortunately, the park board did not build permanent facilities—or a peninsula into Lake Harriet—to accommodate a passing fad.
David C. Smith
© David C. Smith
Minneapolis Park Memory: Ski Jumping at Wirth Park
I have received several very interesting comments from Jim Balfanz on my post about the history of ski jumping in Minneapolis. Today he sent me this photo of him (left) and his brother John, both champion skiers, in a double jump at Wirth Park in 1956. Jim copied the photo from the West High School yearbook of 1956. The original photo was “courtesy of the Minneapolis Tribune.”
In his comments, Jim has provided the names of many people who were important in Minneapolis ski jumping at a time when Minneapolis was producing national champions and Olympians.
If anyone else has memories, stories or photos to add either as comments on that post or in e-mails to me, I’d be delighted to post them.
Thanks to Jim and also to Jay Martin for his comments.
David C. Smith
The Re-creation of Hall’s Island: Part I
Before he saved enough money to go to medical school, Pearl Hall’s job as a teenager in the mid-1870s was pitching wood onto a cart at a lumber yard near the Plymouth Avenue Bridge on the east bank of the Mississippi River. He remembered vividly from those days of hard labor what he called a little steeple of land sticking out of the Mississippi near the bridge. He could see the tiny patch of ground when he stood on top of his loaded wagon–and he saw the little steeple gradually grow.
What Pearl Hall saw from his perch of pine was the beginning of Hall’s Island, the island that as Dr. P. M. Hall he would eventually acquire and turn over to the city, the island that became the site of a popular municipal bath house, the island that eventually was dredged onto the east bank of the great river, and the island that the Minneapolis park board will soon begin to re-create as the first step in its RiverFIRST development plan.
Hall didn’t think about that little speck of land again until he was elected to be Minneapolis’s Health Officer in 1901. Then he wrestled with the problem all health officers everywhere wrestled with and usually lost to: how to dispose of garbage. Not just coffee grounds, melon rinds, and chicken bones, but real garbage — offal, dead horses, night soil — where death could take took root and grow. Read more
What Happened to John Bradstreet’s Japanese Temple in Lake of the Isles?
One hundred years ago the Minneapolis park board lost a Japanese temple and garden with a graceful torii gate and stone lanterns called ishidoro. It’s hard to say who lost it or why it was lost, or even precisely when; we know only that it disappeared sometime around a century ago. It would have been the centerpiece of a popular Minneapolis attraction — smack in the middle of Lake of the Isles. Read on…
Minneapolis Park Memory: More Folwell Football
In September of ’63 dad dropped off Mike Boe and myself at Folwell for Pee Wee football. We were coached by Bob Shogren a corpulent but athletic looking guy who showed up at our practices in a big yellow cab. Word was that Bob had signed with the Cowboys, but had a knee problem that ended his career. Bob seemed to know what he was doing, and taught us about ‘dives’, ‘cross-bucks’, ‘sweeps’, and ‘reverses.’ We learned the idiosyncrasies of the ‘safety’ and the ‘on-side’ kick.
Saturday morning, 45 minutes before kickoff we would assemble in the Folwell pavilion, a strange salmon-colored stucco structure built into a hillside in the middle of the park for the weigh in. Pee Wees could weigh no more than 100 lbs without equipment. A couple of the guys, had a heck of a time making weight.
We then slipped into our gear, a helmet, jersey, and shoulder pads. Football pants were optional, and if they did appear they were the tan canvas ones right out of Norman Rockwell.
This left the game, which consisted of 4 seven-minute quarters, played on a hard pan field marked with powdered lime or pea gravel. We played with a yellow Penn Rubber Co. black striped football, which I never saw any where else.
Two high school-age refs and a volunteer chain gain kept things in order as the assembled parents on the sideline cheered us on and we all enjoyed what at that age was a simple and nonviolent game.
Jim Krave
Thanks for the memory, Jim.
Yard and Garden Show: Trees in Minneapolis
I’ll be the entertainment on the Yard and Garden Show, Saturday, February 4 at noon on WCCO radio, 830 AM. I’ll talk about how the Minneapolis park board became responsible for all the street trees in the city. Did you know that most of Minneapolis south and west of the Mississippi was once open prairie? Then where did all these trees come from? The park board planted most of the trees along our streets—and still owns them. But did you know that’s also one reason the Minneapolis park board has its own police force? Of course, Charles Loring deserves most of the credit; his love of trees was well-known.
Portius Deming, writing in the park board’s 1916 annual report, described a major event that year that so logically connected Loring and trees:
It was a splendid idea to convert the conventional “Arbor Day” into “Charles M. Loring Day,” and it is to the credit of Minneapolis that this suggestion met with instant and universal approval.
“Loring Elms” were planted and dedicated to Loring by children at 78 public schools in the city that day and the Mayor planted a “Loring Elm” in Loring Park. Loring was in his 80s at the time and was still at his winter home in Riverside, California, but his papers at the Minnesota Historical Society include many telegrams he received from well-wishers that day.
Learn more at noon Saturday. Perhaps I’ll recap here afterward.
David C. Smith
 Comments (3)
Comments (3)







